The Third Punic War was a defining event in ancient Rome's history, marking the final chapter in the long-standing rivalry between Rome and Carthage. This war was not only a clash of empires, but it also had far-reaching consequences that shaped the political and cultural landscape of the Mediterranean region. In this article, we will examine the causes and consequences of the Third Punic War, shedding light on its significance in ancient history and its relevance in modern times.
Background of the Third Punic War
To understand the Third Punic War, it is essential to first look at the context of the First and Second Punic Wars. These previous conflicts had established Rome as the dominant power in the Mediterranean, while also sowing the seeds of animosity between Rome and Carthage. The defeat of Carthage in the Second Punic War, led by the infamous Hannibal, fueled the tensions that ultimately erupted into the Third Punic War.
Causes of the Third Punic War
While the previous wars had ended in defeat for Carthage, it had not been completely destroyed. This left Rome with a lingering fear and desire to ensure the complete annihilation of their rival. Additionally, economic and territorial motivations, as well as the role of the Roman Senate and public opinion, fueled Rome's thirst for war with Carthage.
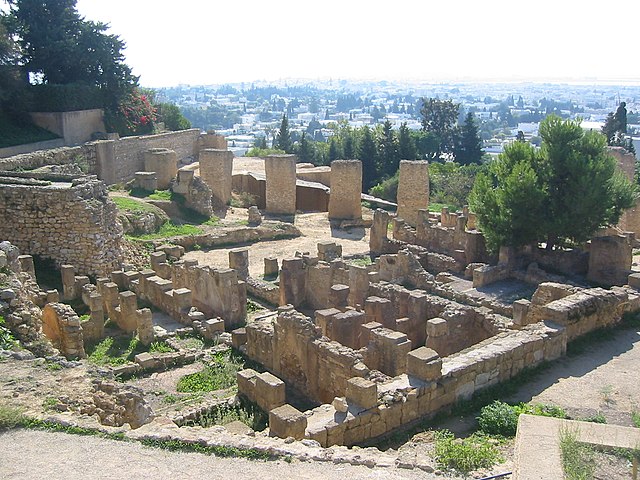

The Course of the Third Punic War
The Third Punic War was marked by major military campaigns and battles, with both sides utilizing different strategies and tactics. However, the Roman siege of Carthage and their ultimate victory proved to be a significant turning point in the war.
Consequences of the Third Punic War
The Third Punic War resulted in widespread destruction and devastation, particularly for Carthage. The loss of territory and resources greatly weakened the once-powerful empire. On the other hand, Rome emerged even stronger and more dominant in the Mediterranean, solidifying their status as the leading power.
Legacy of the Third Punic War
The Third Punic War left a lasting legacy, shaping the political and cultural landscape of the region for centuries to come. It also holds valuable lessons on diplomacy, unchecked expansion, and the role of propaganda in inciting war.
Lessons Learned from the Third Punic War
This war serves as a cautionary tale on the dangers of imperial ambitions and the importance of seeking diplomatic solutions to conflicts. It also highlights the influence of public opinion in shaping the course of history.
Conclusion: The Third Punic War marked a significant turning point in ancient history. It had far-reaching consequences that continue to resonate in modern times. By examining this event, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of war and its impact on societies. Remembering the lessons learned from the Third Punic War can help us avoid repeating the mistakes of the past.
Background of the Third Punic War
The Third Punic War is a significant event in the history of ancient Rome, marking the final conflict between the Roman Republic and its rival, Carthage. The war lasted from 149 BC to 146 BC and resulted in the complete annihilation and destruction of Carthage. Its impact on Rome and the Mediterranean region was immense, shaping the political, cultural, and economic landscape for years to come.
To understand the Third Punic War, we must first look at the two previous wars between Rome and Carthage – the First and Second Punic War. The First Punic War (264 BC-241 BC) was fought over control of Sicily, with Rome emerging as the victor and gaining control of the island. The Second Punic War (218 BC-201 BC) was a much more significant conflict, sparked by Hannibal Barca's invasion of Italy and his victories against the Romans in battles such as Cannae. Despite initial setbacks, Rome eventually emerged as the victor and imposed harsh terms on Carthage, including massive reparations and the surrender of its fleet.
The defeat in the Second Punic War left Carthage weak and vulnerable, but Rome's dominance and growing power created a sense of resentment among the Carthaginians. The political and cultural tensions between the two powers continued to escalate, with Rome viewing Carthage as a threat to its dominance in the Mediterranean region.
The Roman Senate saw an opportunity to destroy Carthage once and for all when the Numidian king, Massinissa, encroached upon Carthaginian territory. Rome, eager to expand its own territory and resources, supported Massinissa's actions and declared war on Carthage. The Senate's decision was also influenced by public opinion, with many Romans still harboring resentment towards Carthage for its previous defeats.
The economic and territorial motivations behind Rome's desire for war with Carthage cannot be overlooked. Carthage's extensive trade and expansion into areas of interest to Rome's allies and territories threatened Rome's economic and political dominance. The Roman Senate saw the destruction of Carthage as a means of securing its power and eliminating a potential rival.
The course of the Third Punic War saw a series of military campaigns and battles, with both sides determined to emerge victorious. The Roman army, led by Scipio Aemilianus, utilized their superior military tactics and siege techniques to slowly weaken and destroy Carthage. The Carthaginians, under the leadership of Hasdrubal and the famous general, Hannibal, fought fiercely but were ultimately unable to withstand Rome's organized and disciplined army.
In 146 BC, after three years of fighting, Rome finally succeeded in their goal of destroying Carthage. The city was sacked, its people killed or enslaved, and the land plowed over to symbolize its complete annihilation. This brutal end to the Third Punic War left a lasting impact on both sides, with Carthage's loss of territory and resources leading to its decline and eventual disappearance from history.
For Rome, the Third Punic War resulted in increased power and wealth, solidifying its dominance in the Mediterranean region. The war also had significant cultural implications, with Roman architecture, art, and literature influenced by the conquest of Carthage.
In conclusion, the Third Punic War was a pivotal event in ancient Rome's history, with far-reaching consequences for both sides. Its causes were rooted in economic and territorial ambitions, fueled by political tensions and public opinion. The war's legacy is one of caution and the importance of diplomacy and compromise in avoiding destructive conflicts. The lessons learned from the Third Punic War continue to be relevant in modern times, reminding us of the dangers of unchecked expansion and the power of propaganda in inciting war and fostering conflict.
Causes of the Third Punic War
The Third Punic War was a significant event in ancient Rome's history, marked by a destructive conflict between Rome and its rival city-state, Carthage. As the third and final war between these two powerful empires, it had a lasting impact on the political and cultural landscape of the Mediterranean region. In this section, we will examine the various causes that led to this war and the consequences that followed.
Economic and Territorial Motivations:
One of the primary causes of the Third Punic War was Rome's desire for economic and territorial expansion. After the defeat of Carthage in the Second Punic War, Rome emerged as the dominant power in the Mediterranean. However, this victory also created a sense of insecurity and greed within the Roman Republic, leading to a desire for further conquests.
The Carthaginian city-state was known for its wealth and dominance in trading networks, which were seen as threats to Rome's economic interests. Rome feared that Carthage's expansion and trade would undermine its control over its allies and territories, thus justifying a preemptive strike against their rival.
Role of the Roman Senate and Public Opinion:
The Roman Senate, the governing body of the Republic, played a crucial role in pushing for war against Carthage. Senate members were primarily composed of wealthy landowners who stood to gain from further conquests. They used their influence to sway public opinion, portraying Carthage as a dangerous enemy that needed to be eliminated.
The Roman people, who were already weary of war after the Second Punic War, were also easily swayed by propaganda and rhetoric from the Senate. The public's support for the war was crucial in securing political and financial resources for the conflict.
Cultural and Political Tensions:
The Third Punic War was a result of long-standing cultural and political tensions between Rome and Carthage. These two city-states had a history of rivalry and conflict, dating back to the First Punic War. The memory of Carthaginian general Hannibal's invasion of Italy during the Second Punic War was still fresh in the minds of the Romans, creating a sense of animosity and revenge towards Carthage.
Moreover, Carthage's cultural differences with Rome, such as their Phoenician origins and practice of human sacrifice, further fueled the idea that they were uncivilized and barbaric, justifying Roman aggression.
Impact of Carthaginian Expansion:
Carthage's expansion was seen as a direct threat to Rome's interests, leading to their decision to go to war. The city-state had gained control over several territories, including parts of modern-day Spain, which were previously under Roman influence. This further increased tensions between the two empires and provided a justification for Rome's desire for territorial expansion.
In conclusion, the Third Punic War was primarily driven by Rome's economic and territorial ambitions, fueled by political and cultural tensions with Carthage. The role of the Roman Senate and public opinion was also crucial in pushing for war. In the next section, we will discuss the course of the war, including the major military campaigns and battles that took place.
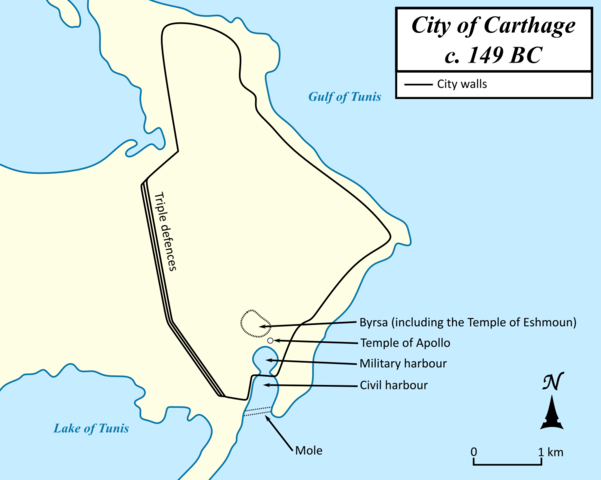
The Course of the Third Punic War
The Third Punic War was a devastating conflict that took place between the ancient superpowers of Rome and Carthage from 149 BC to 146 BC. It was the final chapter in the long-standing rivalry between these two civilizations, and its outcome would have far-reaching consequences for the Mediterranean region.
The war was sparked by Rome's growing desire for economic and territorial expansion, as well as its lingering resentment towards Carthage following their defeat in the Second Punic War. The Roman Senate, along with public opinion, played a crucial role in pushing for war against Carthage.
The course of the Third Punic War can be divided into three major phases: the initial Roman invasion, the siege of Carthage, and the final Roman victory.
The first phase of the war saw Roman forces led by Scipio Aemilianus invading Carthaginian territory in modern-day Tunisia. The Romans quickly gained the upper hand, conquering several key cities and forcing the Carthaginians to retreat to their capital city of Carthage.
The second phase of the war was marked by the siege of Carthage, which lasted for three long years. The Romans surrounded the city and cut off its supply lines, launching a relentless assault on its walls and defenses. During this time, both sides suffered heavy casualties, but the Romans were determined to see the war through to the end.
In 146 BC, the third and final phase of the war began with the fall of Carthage. After months of intense fighting, the Romans finally breached the city's defenses and launched a full-scale assault. The remaining Carthaginian forces, led by their defiant leader, Hasdrubal, fought fiercely but were ultimately overwhelmed by the Roman army.
The Roman victory marked the end of the Third Punic War and the destruction of Carthage. The city was burned to the ground, and its citizens were either killed or enslaved. The war had left a trail of devastation and destruction, which would have a lasting impact on both Rome and Carthage.
The consequences of the Third Punic War were far-reaching. For Carthage, it meant the end of their civilization. The loss of their territory and resources left them weakened and vulnerable, unable to ever rise again as a major power. On the other hand, the war brought great wealth and power to Rome, solidifying its position as the dominant force in the Mediterranean.
The legacy of the Third Punic War is still felt today. It played a significant role in shaping the political and cultural landscape of the Mediterranean region, and its lessons are still relevant in modern times. The war serves as a cautionary tale about the dangers of unchecked expansion and the devastating consequences of war.
In conclusion, the Third Punic War was a brutal and destructive conflict that forever changed the course of history. It highlighted the importance of diplomacy and compromise in avoiding destructive conflicts, as well as the dangers of imperial ambitions and propaganda in inciting war. Understanding this historical event and its consequences is crucial in preventing similar conflicts in the future.
Consequences of the Third Punic War
The Third Punic War, also known as the Final War, was a pivotal event in ancient Rome's history that had significant consequences for both the victor and the defeated. After two previous wars with Carthage, Rome emerged victorious in the Third Punic War, resulting in the complete destruction of the Carthaginian city and empire. In this section, we will discuss the consequences of the Third Punic War on both sides, highlighting the devastation and long-lasting impact of this conflict.
Destruction and Devastation:
One of the most significant consequences of the Third Punic War was the destruction and devastation caused by the conflict. The siege of Carthage by the Roman army resulted in the city being completely demolished and the population either killed or enslaved. The once-great Carthaginian civilization was reduced to ruins, and the Carthaginian people were left with nothing.
On the Roman side, the war also took a toll, with many soldiers losing their lives in battle. The costs of the war also drained the Roman treasury, leading to economic struggles for the empire. However, these consequences were minimal compared to the devastation faced by the Carthaginians.
Impact on Carthage:
The consequences of the Third Punic War were severe and long-lasting for Carthage. The city was completely destroyed, and its territories were annexed by Rome, leaving the Carthaginians with no homeland. The survivors were sold into slavery or fled to other parts of the Mediterranean, scattering the once-great civilization.
The loss of Carthage also had a significant impact on the Mediterranean trade, as it was a major trading center. The loss of this trade hub disrupted the region's economy and resulted in a significant decline in wealth and power for the Mediterranean nations.
Repercussions for Rome:
For Rome, the consequences of the Third Punic War were quite different. The victory over Carthage solidified Rome's position as the dominant power in the Mediterranean region. The annexation of Carthaginian territories provided Rome with more resources and territory, leading to increased wealth and power for the empire.
Furthermore, the defeat of Carthage also erased any threat of future conflicts with the Carthaginians, allowing Rome to focus its attention on other territories and expansion. This victory also boosted the morale of the Roman people and strengthened their loyalty to the empire.
Legacy of the Third Punic War:
The legacy of the Third Punic War is far-reaching and has had a lasting impact on ancient Rome and the Mediterranean region. With the defeat of Carthage, Rome solidified its position as the dominant power in the Mediterranean, paving the way for its future expansion and dominance.
The destruction of Carthage also served as a warning to other nations about the consequences of challenging Roman power. This legacy of fear and respect for Rome would last for centuries to come and shape the political and cultural landscape of the Mediterranean region.
Lessons Learned:
The Third Punic War also holds important lessons for us today. The war highlighted the dangers of unchecked expansion and imperial ambitions, as well as the devastating consequences of war. It also serves as a reminder of the importance of diplomacy and compromise in avoiding destructive conflicts.
Additionally, the role of propaganda and public opinion in inciting war and fostering conflict cannot be ignored. The Third Punic War serves as a cautionary tale of how manipulation and misinformation can push nations towards destructive conflicts.
In conclusion, the consequences of the Third Punic War were far-reaching and had significant impacts on both Rome and Carthage. The destruction and devastation caused by the war, along with the lasting legacy and lessons learned, highlight the importance of understanding this historical event and its relevance in modern times. It serves as a reminder of the dangers of excessive power and the need for diplomatic solutions to conflicts.
Legacy of the Third Punic War
The Third Punic War may have ended over 2,000 years ago, but its legacy still reverberates in our modern world. This war, waged between two powerful empires, Rome and Carthage, has left a lasting impact on the political and cultural landscape of the Mediterranean region. From the destruction and devastation it caused to the lessons learned, the Third Punic War is a significant event in human history that continues to hold relevance today. One of the most significant legacies of the Third Punic War is the rise of Rome as a dominant world power.
With the defeat of Carthage, Rome emerged as the undisputed ruler of the Mediterranean region and continued to expand its territory and influence. The victory over Carthage also brought immense wealth and resources to Rome, solidifying its position as a superpower. This legacy of military conquest and expansion has had a lasting impact on the development of the Western world. The war also had a profound impact on Carthage.
The city was completely destroyed, and its people were either killed or enslaved. This marked the end of the once-great Carthaginian civilization. The loss of Carthage had far-reaching consequences, not just for the city and its people but for the entire region. It left a power vacuum that was quickly filled by the growing Roman empire, leading to further conflicts and conquests. The destruction of Carthage also had a significant impact on the cultural landscape of the Mediterranean, as the influence of Carthaginian art, literature, and philosophy was lost.
Moreover, the Third Punic War also had a lasting impact on the relationship between Rome and its conquered territories. The war had shown the ruthlessness and ambition of Rome, causing fear and distrust among its allies. This ultimately led to rebellions and uprisings against Roman rule, as conquered peoples feared facing a similar fate as Carthage.
The legacy of the Third Punic War serves as a cautionary tale about the consequences of unchecked power and imperial ambitions. In addition to the political and cultural impact, the Third Punic War also holds valuable lessons for modern times. The war highlights the dangers of propaganda and public opinion in inciting conflict and promoting destructive nationalism. It also showcases the importance of diplomacy and compromise in avoiding destructive wars.
The Third Punic War serves as a reminder of the devastating consequences of war and the need for peaceful resolutions. In conclusion, the Third Punic War has left a profound legacy on the ancient world and continues to hold relevance in our modern times. It shaped the political and cultural landscape of the Mediterranean and left a lasting impact on the rise of Rome.
However, it also serves as a warning about the dangers of unchecked power and the importance of diplomacy and compromise in resolving conflicts. The lessons learned from the Third Punic War are still relevant today, making it a crucial event to study and understand in order to prevent similar tragedies from occurring in the future.
The legacy of the Third Punic War reminds us of the cyclical nature of history, and the importance of learning from the past to shape a better future.
Lessons Learned from the Third Punic War
As with any major historical event, the Third Punic War has left behind valuable lessons that can be learned and applied even in modern times. This destructive conflict between two powerful empires, Rome and Carthage, serves as a cautionary tale of the consequences of unchecked expansion and imperial ambitions. In this section, we will delve into the key lessons that can be drawn from the Third Punic War and their relevance in today's world.
- The Importance of Diplomacy and Compromise:
One of the main causes of the Third Punic War was the breakdown of diplomacy and compromise between Rome and Carthage. Despite previous attempts at peace, the Romans, fueled by their desire for power and resources, refused to negotiate and instead chose to go to war. This led to a devastating conflict that resulted in the annihilation of Carthage. The lesson here is that diplomatic efforts and willingness to compromise can prevent destructive conflicts and lead to lasting peace.
- The Dangers of Unchecked Expansion:
The Third Punic War was a result of Rome's insatiable appetite for expansion and conquest. The Romans viewed Carthage as a threat to their growing empire and saw the need to eliminate it. However, this unbridled expansion ultimately led to the destruction of both empires. This serves as a reminder that unchecked expansion and imperialism can have disastrous consequences, not just for the targeted nation but also for the aggressor.
- The Role of Propaganda and Public Opinion:
During the Third Punic War, the Roman Senate and public opinion played a significant role in pushing for war against Carthage. Propaganda and false narratives were used to justify the conflict and rally support from the citizens. This highlights the power of propaganda and how it can manipulate public opinion and incite war and conflict. It is crucial to critically analyze information and not fall prey to propaganda for the sake of peace and stability.
- Lessons for Modern Times:
Although the Third Punic War happened over two thousand years ago, its lessons are still relevant in today's world. As nations continue to compete for power and resources, it is essential to remember the destructive consequences of war and the importance of diplomacy, compromise, and peaceful resolution of conflicts. The Third Punic War also serves as a warning against imperialistic ambitions and the need for responsible leadership in a globalized world.
In conclusion, the Third Punic War was a significant event in ancient Rome's history, with far-reaching consequences for both empires involved. However, it also serves as a source of valuable lessons that can guide us in navigating modern-day conflicts. From the dangers of unchecked expansion and imperialism to the importance of diplomacy and the dangers of propaganda, the Third Punic War continues to hold relevance and significance in our understanding of history and the world around us. Let us remember these lessons and strive for peace and understanding in our interactions with others.
